Breast cancer is a prevalent and significant health concern globally, affecting millions of individuals each year. Understanding its causes, risk factors, and key facts is essential for early detection, treatment, and prevention efforts. Buy raloxifene online is a medicine used to treat postmenopausal osteoporosis and the gamble decrease of obtrusive bosom malignant growth in post-menopausal women.
Here’s a comprehensive guide covering common causes of breast cancer and important facts about this disease:
Common Causes of Breast Cancer:
1. Genetic Factors:
- BRCA Gene Mutations: Inherited mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes significantly increase the risk of breast cancer. Women with these mutations have a higher likelihood of developing breast cancer at a younger age. Raloxifene 60 mg tablet is helps in minimizing the risk of developing invasive breast cancer in women.
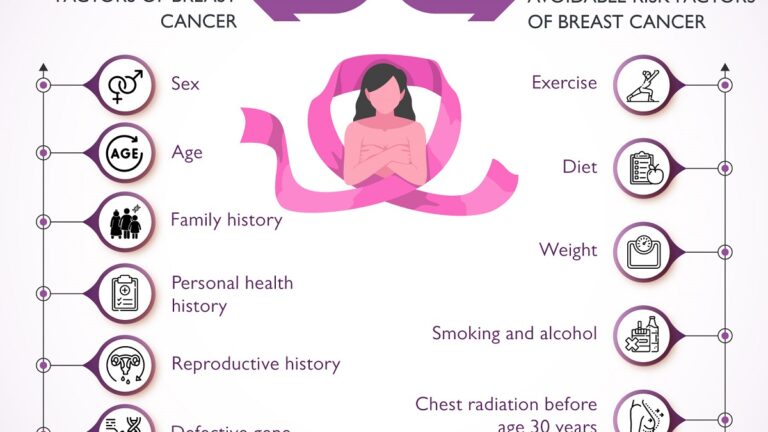
- Family History: A family history of breast cancer (especially in first-degree relatives) can increase an individual’s risk, indicating a genetic predisposition.
2. Hormonal Factors:
- Estrogen Exposure: Prolonged exposure to estrogen, whether naturally (early menarche, late menopause) or through hormone replacement therapy (HRT), can elevate the risk of breast cancer.
- Reproductive Factors: Early onset of menstruation (before age 12), late onset of menopause (after age 55), and never giving birth or having the first child after age 30 are associated with increased risk.
3. Lifestyle and Environmental Factors:
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese after menopause increases the risk of breast cancer, likely due to higher estrogen levels produced by fat tissue.
- Alcohol Consumption: Regular and excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular physical activity may contribute to a higher risk of breast cancer.
- Environmental Exposures: Exposure to certain chemicals, radiation (including previous radiation therapy to the chest), and environmental pollutants may increase breast cancer risk.
4. Age and Gender:
- Age: The risk of breast cancer increases with age, with the majority of cases occurring in women aged 50 and older.
- Gender: While breast cancer primarily affects women, men can also develop breast cancer, though it is much less common.
5. Other Risk Factors:
- Dense Breast Tissue: Women with dense breast tissue have a higher risk of breast cancer.
- Previous Breast Cancer: A history of breast cancer increases the risk of developing cancer in the opposite breast or a new cancer.
- Personal Health History: Certain benign breast conditions (e.g., atypical hyperplasia) can increase the risk.
- Race and Ethnicity: Breast cancer incidence and outcomes can vary among different racial and ethnic groups.
Key Facts About Breast Cancer:
1. Incidence and Prevalence:
- Global Impact: Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases diagnosed in 2020 alone.
- High Incidence in Developed Countries: Developed regions generally have higher breast cancer rates compared to developing countries, attributed to lifestyle factors and early detection practices.
2. Screening and Early Detection:
- Mammography: Regular mammograms are crucial for early detection, which significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates.
- Clinical Breast Exams: Regular clinical breast exams by healthcare providers are recommended for early detection in addition to mammograms.
3. Types of Breast Cancer:
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS): Early-stage cancer where abnormal cells are found in the lining of a breast duct.
- Invasive Breast Cancer: Cancer that has spread from where it began in the breast ducts or lobules to surrounding normal tissue.
4. Treatment Options:
- Surgery: The main treatment for breast cancer involves surgical removal of the tumor (lumpectomy or mastectomy) and possibly lymph nodes.
- Radiation Therapy: Used to destroy cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence after surgery.
- Chemotherapy and Hormone Therapy: Depending on the type and stage of breast cancer, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy, or a combination may be recommended.
5. Survival Rates:
- Early Diagnosis: Early-stage breast cancer has a higher likelihood of successful treatment and long-term survival.
- Survivorship: Many women and men diagnosed with breast cancer go on to live long, healthy lives with appropriate treatment and follow-up care.
6. Advancements in Research:
- Genetic Testing: Advances in genetic testing help identify individuals at higher risk and inform personalized treatment decisions.
- Targeted Therapies: Targeted therapies and immunotherapy are emerging as effective treatments for specific types of breast cancer.
Conclusion:
Understanding the causes and key facts about breast cancer is crucial for prevention, early detection, and effective treatment. By raising awareness, promoting regular screening, adopting healthy lifestyle choices, and supporting ongoing research, we can continue to improve outcomes for individuals affected by breast cancer worldwide. If you or someone you know has concerns about breast health or risk factors, consulting with a healthcare provider is important for personalized risk assessment and management strategies. Early intervention and comprehensive care play vital roles in reducing the impact of breast cancer on individuals and communities.